FUNDAMENTALS OF COMPUTER STUDIES PART-1
Computer as a
revolution left no area of left untouched in the present world. It is of
tremendous help in all field of life. Hence, the knowledge of computer is a
necessity for existence of everybody in his global village. The invention o
computer has transformed our simple manual works to sophisticated life of
automated work to meet the global demand for the higher productivity and
increase efficiency with high precision.
Computer is increasingly becoming compulsory in nearly all
fields of studies, not because of anything but its accuracy and versatility in
processing data. Many tasks at home or office are being automated rapidly with
computer. Thus it is becoming apparent that in whatever discipline or working
sector, the computer is now a very vital tool for efficiency improvement and
precision of job or task execution.
This is designed to meet the prerequisite need of everybody
that are interested and wish to know about computers science and computing in
general.
A computer is an electronic device, operating under the
control of instructions stored in its own memory. These instructions tell the
machine what to do. The computer is capable of accepting data (input),
processing data arithmetically and logically, producing output from the
processing and strong the results for future use. Most computer that sit on a
desktop are called Personal Computers (PCs).
The “computer” is an ensemble of different machines that you
will be using to get your job done. A computer
is primarily made of the Central Processing Unit (usually referred to as
the computer ), the monitor, the keyboard, and the mouse. Other pieces of
hardware are commonly referred to as peripherals.
In everyday life activities, we process data or encounter
cases of data processing. A typical example of data processing is the
generation of statement of student result from marks score in an examination
and continuous assessment. It is
essential to know that information is as
good as data from which it is derived, and the transformation process which the
are subjected to. Meaningless data or inappropriate processing produces wrong
information. Thus computer gives you results corresponding to what data you
supply and how you process it.
Summarily, the intelligent performance of a computer depends
on correctness of input data and the intelligence performance of the human
being that drives it.
People use computers in many ways; business, computer are
used to track inventories with bar codes and scanners, check the credit status
of costumers, and transfer funds electronically, homes, tiny computers embedded
in the electronic circuitry of most appliances control the indoor temperature,
operate home security system, tell the time, and turn video cassette recorders
(VCRs) on and off, automobiles regulate the flow of fuel, thereby increasing
features froma digitally encoded laser disc.
Computer programs, or applications, exist to aid every level
of education, from programs that teach simple addision or sentence communicate
with students; with coputer-controlled projection units, they can add graphics,
sound, and animation to their communications. Computer are used extensively in
scientific research to solve
mathematical problems, investigate complicated data, or model systems that are
too costly or impractical to buld, such as testing the air flow around the next
genration of aircraft. The military employs computers in sophisticate
communications to encode and unscramble messages, and to keep track of
personnel and supplies.
HISTORY OF COMPUTING-
Since the creation of men, a singnificant amount of human
activities has been ascribed to organizing and processing information so that
it could be more easily presented for easy comrehension. Many devises have been
used in the past before the advert of computer. It is then necessary to vividly
look into their evolution. Early computing machines:
1.
Abacuse (-2500BC): This is a hand –hald device
made of heads stung on rods in a fame. The rods correspond to positions of the
digits while the beads correspond to the digits.
2.
Napier’s Bone (-2500BC): This was invented
byJohn Napier’s (1550-1617). The consists of small rods with appropriate
marketings on them. It is a mechanical aid to computation that consists of nine
such rods (called bones) with one for each digit 1 through 9. He also invented
logarithms which made possible to do division and multiplication by performing
addition and subtraction.
3.
Slide Rule (1600AD) by William Oughtred
(1575-660): He invented it in 1622 but announced it in 1632 this consist of
rules on which markings respresent logarithms of number and also permits
calculation involving exponents, trigonometric functions, ect.
4.
Pascal
mechenical calculator (1600) or Numerical wheel calculator;-Blaise
Pascal (1623-1664) in 1642 invented the first adding machine called Pascaline.
The brass rectangular box used eight moveable dials to add and sum up of eight
figures long using base 10. It can perform all the four arithmetic operation
with previous unheard speed.
1. Leibnitz mechanical multiplier (1600): In 1694
Gottifrided Wilhem Von Leibnitz (1646-1716) improved upon the pascaline by
creating a machine that can also multiply using a system of deals and gear.
2.
Colmar’s Calculator (1820) by Charles Xavier
Thomas de Colmar: This present a more practical approach to computing.
3.
Punches-Card mechine (Jacquard’s Loom)
(1801): Joseph Marie Jacquard.
4.
Mecanical computer: Charles Gabbage (1792-1871)
Father of the computer : Difference endine powered by steam and large as
locomotive the machine has a stored program and could perform calculations and
point the result automatically. We also have Analytical engine credited to him.
5.
Hermann’s Hollerith (1860-1929)
ü
Hollerith’s systempunch-card reader machine:-for
counting census result in 1890 in US.
ü
Formed tabulating machine company in 1896 (TMC)
ü
Automatic Tabulating Machine (ATM)-1900
ü
TMC was renamed to International Business
Machines Corporation (IBM) in 1924 after series of mergers.
In summary, the history of
computing began with an analog machine. In 1623 German scientist Wilhelm
Schikard inverted a machine that could add, and with the aid of logarithm
tables, multiply and divide. Since them the devlopment has pass through a lot
of stages such as the invention of punched cards to program patterns to create
women fabrics by Joseph-Marie Jacquard a French inventor in 19th
century. Another early mecanical computer was the Different Engine, designed in
the early 1820s by British mathematician and scientist Charles Babbage. In the
1930s American mathematician Howard Aiken developed the Marek 1 caculating
machine, Which was built by IBM This elecronic calculating machine used relays
and electromagnetic components to replace mechanical components.
To be sincere, the world has left
the era of hearing stories about coputer. We are now in the world of what you
can use it for to serve its desired purposes.
GENRATIONS OF COMPUTER-
The history of
computer development is often referred to in refference to the different genrations
of computing devices. Each genration of computer is characterized by a major
technological development that fundamentally changed the way computer oprete,
resulting in increasingly smaller, cheaper, more powerful, efficient and
reliable device.
·
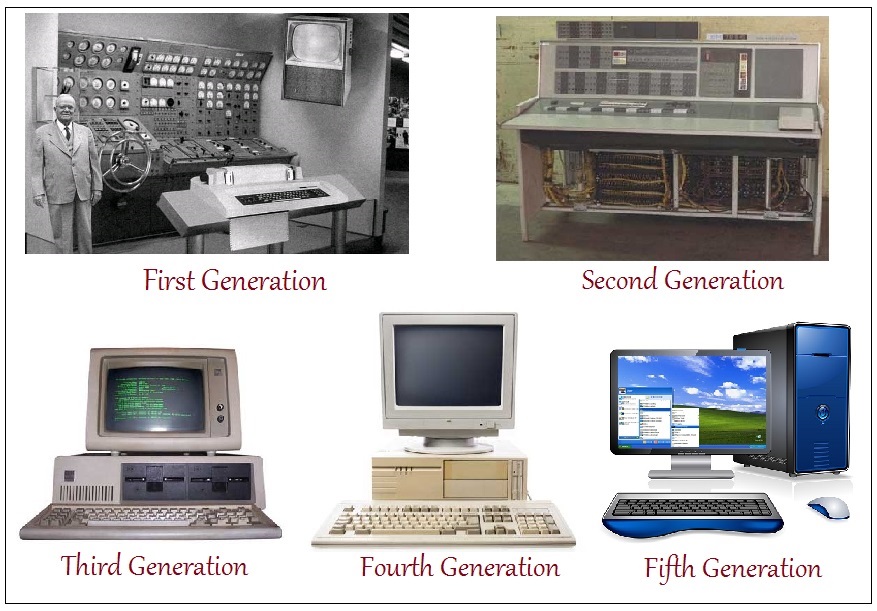
FIRST
GENERATION-1940-1956: VACUUM TUBES:-
The first computers used vacuum tubes for
circuity and madnetic drums for memory,and
were often enomous, taking up entrie rooms. They were very expensive to
opreting and in addition to using a great deal of electricity, genrated a lot
of heat, Which was often the often the cause of malfunctions. First genration
computers relied on machine language to performe operations, and they could only
solve one problem al a time. Input was based on punched cards and paper tape,
and output was displayed on printouts. The UNIVAC and ENIAC COMPUTERSARE examples of first-genration computing device.
The UNIVAC was the first commercial computer deliverd to a business client. It
was used in the 1951U.S. Bureau Census.
Second Generation - 1956-1963: Transistors
Transistors replaced vacuum tubes and ushered in the second generation of computers. The transistor
was invented in 1947 but did not see widespread use in computers until the late 50s. The transistor was a vast
improvement over the vacuum tube, allowing computers to become smaller, faster, cheaper, more energyefficient
and more reliable than their first-generation predecessors. Second-generation computers still relied on
punched cards for input and printouts for output. Second-generation computers moved from cryptic binary
machine language to symbolic, or assembly, languages, which allowed programmers to specify instructions in
words. High-level programming languages were also being developed at this time, such as early versions of
COBOL and FORTRAN. These were also the first computers that stored their instructions in their memory,
which moved from a magnetic drum to magnetic core technology. The first computers of this generation were
developed for the atomic energy industry.
Third Generation - 1964-1971: Integrated Circuits
The development of the integrated circuit was the hallmark of the third generation of computers.
Transistors were miniaturized and placed on silicon chips, called semiconductors, which drastically increased
the speed and efficiency of computers. Instead of punched cards and printouts, users interacted with third
generation computers through keyboards and monitors and interfaced with an operating system, which allowed
the device to run many different applications at one time with a central program that monitored the memory.
Computers for the first time became accessible to a mass audience because they were smaller and cheaper than
their predecessors.
Fourth
Generation - 1971-Present:Microprocessors
The
microprocessor brought the fourth generation of computers, as thousands of
integrated circuits were built
onto a single silicon chip. What in the first generation filled an entire room
could now fit in the palm of the hand. In 1981 IBM introduced its first
computer for the home user, and in 1984 Apple introduced the Macintosh.
Microprocessors
also moved out of the realm of desktop computers and into many areas of life as
more and more everyday products began to use microprocessors.
As these small computers became more powerful,
they could be linked together to form networks, which eventually led to the development
of the Internet. Fourth generation computers also saw the development of GUIs,
the mouse and handheld devices.
Fifth Generation
- Present and Beyond: Artificial Intelligence
Fifth generation
computing devices, based on artificial intelligence, are still in development,
though
there are some
applications, such as voice recognition, that are being used today.
The use of
parallel processing and superconductors is helping to make artificial
intelligence a reality. Quantum computation and molecular and nanotechnology
will radically change the face of computers in years to come.
The goal of
fifth-generation computing is to develop devices that respond to natural
language input and are capable of learning and self organization.




Very nice bro
ReplyDeleteVery nice
ReplyDelete