FUNDAMENTALS OF COMPUTER STUDIES PART-2
HARDWARE AND SOFTWARE-
Hardware is the team given to the physicaly components of a
computer: e.g. keyboard, monitor, system box or floppy disk drive. Software, on
the other hand, is electronc information: file, operating system, graphics,
computer programs are all example of software. The difference bitween hardware
and software reflects the duality between the physical and mental worls: for
example, your brain is hardware, whereas your mind is software.
Software is the stuff that makes your
computer do things for you. The computer without software would be like a home
entertainment system with no tapes, CD’s, or movies-you have the machine, but
there’s nothing to play on it. Software is continually develops a new version
of their software they assign it a version number: Before Microsoft Word 7,
there was Microsoft Word 6.0.1, and before that Word 6.0. The larger the
developments made to the software, the larger the virson number changes.
Usually a large change will result in a whole number upgrade; a small change
may result in a tenth of a decimal place.
Hardware
are those components or physical pieces (things you can touch) that make up the
computer: The different pieces of the computer’s hardware are monitor,
speakers, mouse, CDROM, floppy drive, hard dreive, keyboard, CPU, RAM,
Processor, etc. Each pieces plays a role in the operation of a computer.
DIFFERENT PARTS OF A
COMPUTER AND THEIR USES.
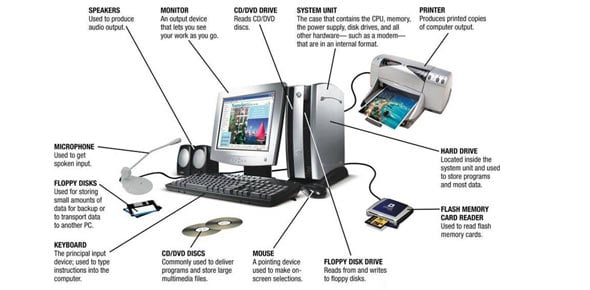 |
| DIFFERENT PARTS OF A COMPUTERS AND THEIR USES |
The
standard computer consists of a monitor, a keyboard, a mouse and the system
unit. One can attach accessories such as printers and scanners by means of
ports. Increasingly in the workplace, computers are connected to printers and
other computers by means of a network.
THE MONITOR-
 |
| MONITOR |
This is the Visual Display Unit (VDU). There are versious
technologies for the display unit, cathode ray tube (CRT) or Liquid Crystal
Display (LCD) or electro luminescent screens or the projector: The monitor or
screen displays your work. Facing it down reduces reflected glare from room
lights. This reflection may affect your sight. Monitors come in different
sizes. The (most important) size of monitor is measured digonally on the screen
(in inches). Based on this, the monitors range in sizes of 12’’, 14’’, 15’’,
17’’, 19’’, 21’’, 29’’, etc. Monitors are also characterized by the flatness of
their screen. The flatter and the wider screens are usually the better.
THE SYSTEM BOX OR
COMPUTER CONSOLE-
 |
| C.P.U |
Central Processing Unit (CPU).
The CPU is a single microprocessor that holds a large number
of circuits.
The CPU receivers data from the ROM, RAM, and keyboard. It
sends data to the RAM for storage, and to output devices, such as the monitor.
THE KEYBOARD
(PRESSING)-
 |
| KEYBOARD |
This is the basic input device. It is one of the ways you can
tell computer what to do. It consists of the standard typewriter keys as well
as a numeric keys. You can use it to give computer commands, name folders and
files, and type text in word processing documents. The keyboard is made of
three main categories of keys with each used for a different purpose.
i. Character Keys: These comprise of letters, numbers
and the symbols. They are used to insert/display readable characters on the screen
which is equivalent to the keystroke pressed.
Letters a,b,c,d,e,f,g,h,I,j,k,l,m,n,o,p,q,r,s,t,u,v,w,x,y,z
Numbers 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9
ii.
Action Keys: these are not used to type anything,
instead they cause an acton. Escape, Tap, Caps Lock, Shift, Control, Alt,
Backspace, Enter, Window, Win Menu, Print Screen, Scroll Lock, Pause break,
Number Lock, Insert , Home, Page Up, Delete, End, Page Down, Power, Sleep, Wake
up, Up Arrow, Left Arrow, Right Arrow, Down Arrow, and Space Bar.
iii.
Application-Dependant Keys: These are called function keys: They
are F1, F2, F3, F4, F5, F6, F7, F8, F9 , F10, F11, and F12. Although the F1 key
is usually to get help while working in Microsoft Windows, the use of the other
keys varies from application to another. Eventually, the application you see
will give you instructions on what to do and how to use the function keys.
KEY COMBINATIONS-
Some keys can be combined to produce uppercase letters or to
access the upper symbols some keys (i.e. the Shift and Control keys). Keys are
also combined for many other reasons. In some situations, you have to press
keys simultaneousl, which means that you may be expected to press two or more
keys at the same time, or almost at the same time. In some other situations,
you may have to press and release one key, followed by another.
SHORTCUTS-
A shortcuts is a quick action you ask a program to perform
when you press one particular key or a combination of keys. Some shortcuts are
universal or almost, that is, the computer responds regardless of what
application is running. Some other shortcuts depend on what you have on your
screen. Some shortcuts are already known to the computer (as part of the
operating system). Most other shortcuts are set by the programmer of the
particular application you are using. Yet some applications allow you to create
your own shortcuts. Some shortcuts are redily obvious and can be seen from the
main menu of the application. Some other shortcuts are either part of Microsoft
Windows (and can be applied in your program) or are not easily displayed, you
might have to search the help socumentation of the program you are using.
THE MOUSE (CLICKING
AND DRAGGING)-
 |
| THE MOUSE (CLICKING AND DRAGGING) |
This is another input device used to moved a small white
arrow pointer-the Cursor (but the shape will change depending on the context in
which the mouse is being used) on the screen. By pointing and clicking you can
carry out commands. The computer may ask you to verify that you are sure to
rename a file, by clicking on the ‘OK’ button. A mouse is primarily made of
three parts: the buttons, the handing area, and the sensor (rolling object or
light). There are either one, two or three mouse buttons. By default, a mouse
has two buttons: left and right. Most mice nowadays are also equipped with
wheel on top of the middel button called the Scroll Button.
To use the mouse, the first decision you make is to know
which of your two hands you will be using to handle the mouse. By default, the
mouse is configured to work for right hand. If you are left-handed, the
settings can be changed to suit your needs: start-Control Panel-Double click
Mouse-on the Buttons Tab, Check the Switch Primary and Secondary Buttons check
box.
You can also change the cursor from the default Up-Left
Pointing to another but you should know that this is best determined by the
computer as this varies from program to program. To change, click the pointer’s
Tab. Also click the other tabs to review the different properties.
Note- the
expression ‘’by default’’ means ‘’if everything is not (yet) changed from the
original or normal settings’’.
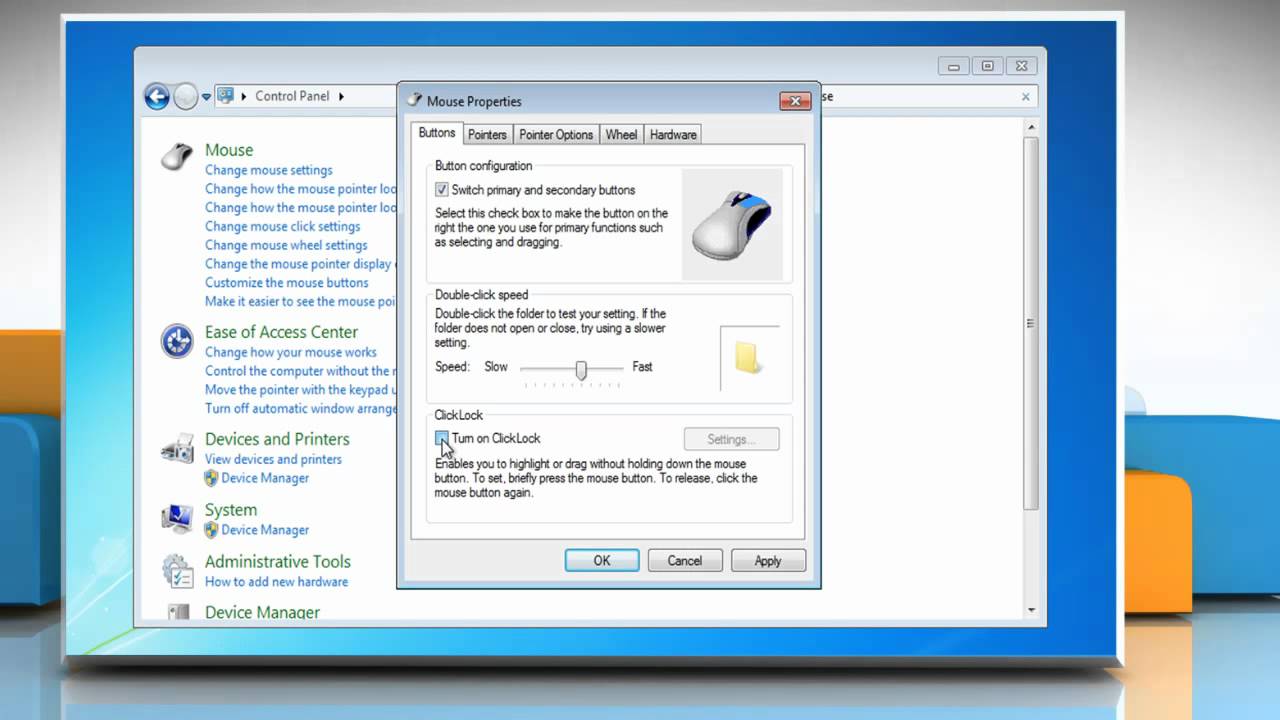 |
| MOUSE PROPERTIES DIALOG BOX |
The tip of the
mouse pointer must be positioned on the item you want to use (Pointing).
To select an item, point to the item and click once (Selection . Left Clicking). Double-clicking
(left button) on an icon invokes a command or launches an application.
Dragging an item (icon or
other object) from one location to another, position the mouse pointer on the
item, click and hold the mouse buttons (left, right) down, and move the item to
the new location.
Right Clicking (right button)
invokes a shortcut (contextual) menu that contains all the actions that are
related to the item. Some applications, namely programs used to manipulate text
(they are
called word
processors), allow you to triple-click.
On Windows machines,
there is a left and right mouse button. Most time you use the left mouse button
(if you are right-handed). On some newer Macs, the same feature can be used with
their single mouse button by holding down the Control key as you click an item
on the screen.
The Peripherals
All the parts we have reviewed so
far are usually required for the computer to function. Some other parts, not required,
can also be connected to the computer to complement it. A peripheral is an
object attached to the computer to help it perform some necessary assignments
none of the other parts can handle. In most scenarios, no peripheral is
required but nowadays, it is unusual for a computer not to have any peripheral
at all. The most used peripherals are the printer, a digital camera, a scanner,
a projector, an external drive (such as an external CD burner for an old
computer), etc.
Disk Size Conversion
Chart (Bits, Bytes, Kilobytes, Megabytes and Gigabytes)
Bit- Binary digit:-a single
elements in the computer memory that can store either 1 or 0
Word . 1Byte, 2Byte or 4Byte depending on the
machine. Generally computer word length is giving in bits; hence we have 8bit,
18bit or 32bit microprocessor computer.
Table 1:
Computer Storage Devices Unit Conversion
Unit Equivalent to
1Byte 8 Bits
1kilobyte (kB) 1,024Byte
1MB 1,024KB = 1,024,000Byte
1GB 1,024MB =
1,024,000,000Byte


Nice
ReplyDeleteIt's
Leader in developing embedded system projects, providing Engineering and SCADA solutions using Raspberry pi, Arduino and more.... transistors
ReplyDeleteHey what a brilliant post I have come across and believe me I have been searching out for this similar kind of post for past a week and hardly came across this. Thank you very much and will look for more postings from you. antminer s17
ReplyDeleteWith that, you have also probably noticed that despite "studying" in such an area, your exam results were not as high as you expected. יועץ השקעות לימודים
ReplyDelete